In this piece of content, we will explain what crawl budget means in SEO and share helpful ways to make it work better for your website.
What Is Crawl Budget in SEO?
Crawl budget in SEO refers to the amount of time and resources that search engines allocate to visit and analyze a website.
It determines how much of a website’s content search engines will crawl and include in their index.
How Does a Crawler Work?
A crawler, also known as a web spider or web robot, is a program used by search engines to explore and collect information from websites. Here’s how a crawler works in simple points:
- Start point: Crawler begins at a web page.
- Visit pages: Crawler follows links to explore web pages.
- Collect info: Crawler gathers content, like text and images.
- Follow links: Crawler keeps moving by following more links.
- Indexing: Search engine organizes and stores the collected information in its database.
- Repeat process: Crawler continues visiting and indexing pages.
- Update process: Crawler revisits pages for changes and updates.
Why Is Crawl Budget Important for SEO?
In simple terms, If Google does not index a webpage, that page won’t rank in Google’s search results.
This is because the webpage does not exist in Google’s indexed database.
In other words, if Google doesn’t know about the page, it won’t show up in search results when people search for relevant topics.
When Google’s crawl budget for your website is exhausted, there will be several pages on your website that Google has not indexed.
These unindexed pages exist because Google’s resources for crawling and indexing your website are limited.
That is why it is important to optimize your website’s crawl budget to ensure that Google indexes the most important and valuable pages of your website.

Benefits of Optimizing Crawl Budget
Below are some major benefits of optimizing crawl budget.
Find and Show Pages:
Search engines need to organize and show web pages in search results.
Optimizing crawl budget helps them do this efficiently.
Discover New Pages:
A good crawl budget helps search engines find new and updated pages on your website quickly, so they can include them in search results.
Show New Content Fast:
With an optimized crawl budget, search engines can find and display new content faster in search results.

Explore More Pages:
A bigger crawl budget lets search engines explore more of your website, so more pages have a chance to appear in search results.
Better SEO Performance:
Optimizing crawl budget helps improve overall SEO performance of a website, which means more people find your website through search engines.
Choose Important Pages:
You can tell search engines to focus on important pages first, so they show up in search results sooner.
Avoid Unimportant Pages:
By managing crawl budget well, you can make sure search engines don’t spend too much time on less important or duplicate content.

Find Crawling Problems:
Monitoring crawl budget helps you identify any issues with crawling, like errors or blocked parts of your website, so you can fix them.
Quick Recovery from Errors:
A well-managed crawl budget helps your website recover faster from technical errors, like server problems, so it stays visible in search results.
Better User Experience:
Optimizing crawl budget improves the experience for people using search engines, as they can find more relevant content and get better search results.

What determines the crawl budget?
There are four main factors that determine your crawl budget:
Crawl demand:
This is how important Google thinks your pages are to its users.
Pages that are more popular, have more links pointing to them, or are updated more frequently will have a higher crawl demand.
Crawl capacity:
This is the amount of resources that Google has available to crawl websites.
This can be affected by factors such as the number of other websites that Google is crawling, the size of your website, and the speed of your server.
Server response time:
Googlebot will spend more time crawling your website if it takes a long time for your server to respond.
This can be caused by factors such as high traffic, a slow server, or a poorly optimized website.

Robots.txt file:
The robots.txt file is a text file that tells Googlebot which pages on your website it can and cannot crawl.
If you have a robots.txt file, Google will only crawl the pages that are allowed.
How to optimize Crawl Budget?
To help with crawl budget optimization, you can follow the points mentioned below:
Enhance server speed and resource allocation
Make your website load faster by improving your server and adding more resources.
This helps search engine bots to explore more pages on your website without using too much of their crawling limit.
Boost link building (More external and internal links)
Create links to your website from other websites (external links) and from one page to another within your own website (internal links).
These links help search engine bots find and explore your website more easily.

Fix Redirected Links
Check and fix any links on your website that redirect users to another page.
Redirects can confuse search engine bots and waste their time.
Fixing them ensures that the bots can crawl your website more efficiently.
Use GET whenever possible instead of POST
When designing your website, try to use GET requests instead of POST requests whenever possible.
GET requests are easier for search engine bots to process and crawl. This is because POST requests use resources every time, while GET requests can be cached for later use.
Leverage the Indexing API
Some search engines like Google and Bing offer an Indexing API, which allows you to directly notify them about new or updated content on your website.
This helps search engines quickly include or update your website content in their search results.
Implement noindex for 304 (Not Modified) pages
Use a special directive called “noindex 304” for web pages that haven’t changed since the last time they were crawled.
This tells search engines not to waste time re-crawling unchanged pages, saving their resources.
Manage URL parameters effectively
Be mindful of the parameters (extra information) in your website’s URLs.
Make sure they are properly managed to avoid creating multiple versions of the same page.
This helps search engines focus on important content.

Avoid HTTP errors to save your crawl budget
Regularly check for and fix any errors that occur when someone tries to access your website.
These errors can waste search engine bots’ crawling resources. Fixing them ensures that your website is crawled effectively.
Update Your Sitemap
Keep your website’s sitemap up to date. A sitemap is like a map that helps search engines find all the pages on your website.
By updating it, you make it easier for search engines to crawl and index content on your website.
Use More HTML
When creating your web pages, try to use HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) instead of other technologies like JavaScript or Flash.
HTML is easier for search engine bots to understand and crawl.

Ensure the importance of hreflang tags
If your website has versions in different languages or targets different regions, use hreflang tags.
These tags help search engines understand which version of your website to show in search results based on the user’s language or location.
How do you set a crawl budget?
Here are the key points to set a crawl budget.
Optimize website architecture:
Create a logical and organized structure with clear categories and internal linking.
XML sitemap:
Generate and submit an XML sitemap to help search engines discover and prioritize important pages.

Robots.txt file:
Use a robots.txt file to guide search engine bots on which areas to crawl and which to exclude.
Monitor crawl activity:
Regularly check crawl statistics using tools like Google Search Console or Bing Webmaster Tools.
Page optimization:
Optimize web pages for faster loading speeds to ensure search engines can crawl content within the allocated time frame.
Quality Content:
Focus on creating valuable and unique content relevant to your target audience.

Backlink profile:
Maintain a healthy backlink profile by monitoring and disavowing spammy or irrelevant backlinks.
Monitor crawl errors:
Check for and fix crawl errors like broken links or server errors that hinder search engine crawling
How to Calculate Crawl Budget?
Calculating crawl budget can be complex, but here are simplified steps:
- Count pages: Determine how many pages are on your website.
- Analyze importance: Identify important pages based on user engagement and relevance.
- Monitor crawl rate: Keep track of how often search engines crawl your site.
- Fix errors: Fix any broken links or issues that prevent search engines from accessing your content.
- Improve site speed: Make your website load faster to ensure efficient crawling.
- Consider backlinks: Pages with more quality links tend to get crawled more.
Remember, crawl budget is not an exact science, but by optimizing these factors, you can improve how search engines crawl your website.

How to Check Crawl Budget?
Checking crawl budget involves understanding how search engines allocate resources to crawl a website. Here’s a simplified explanation with points:
Use search console:
Search engines like Google provide a tool called Search Console. It shows crawl statistics and information about your website’s performance.
Monitor crawl rate:
Check how often search engine bots visit your site. If they come frequently, it indicates a good crawl budget.
Analyze crawl stats:
Look for data on the number of pages crawled per day or per visit. This helps understand how much of your site is being explored.
Check index coverage:
Review the index coverage report in Search Console. It shows which pages are indexed, meaning they are included in search results.
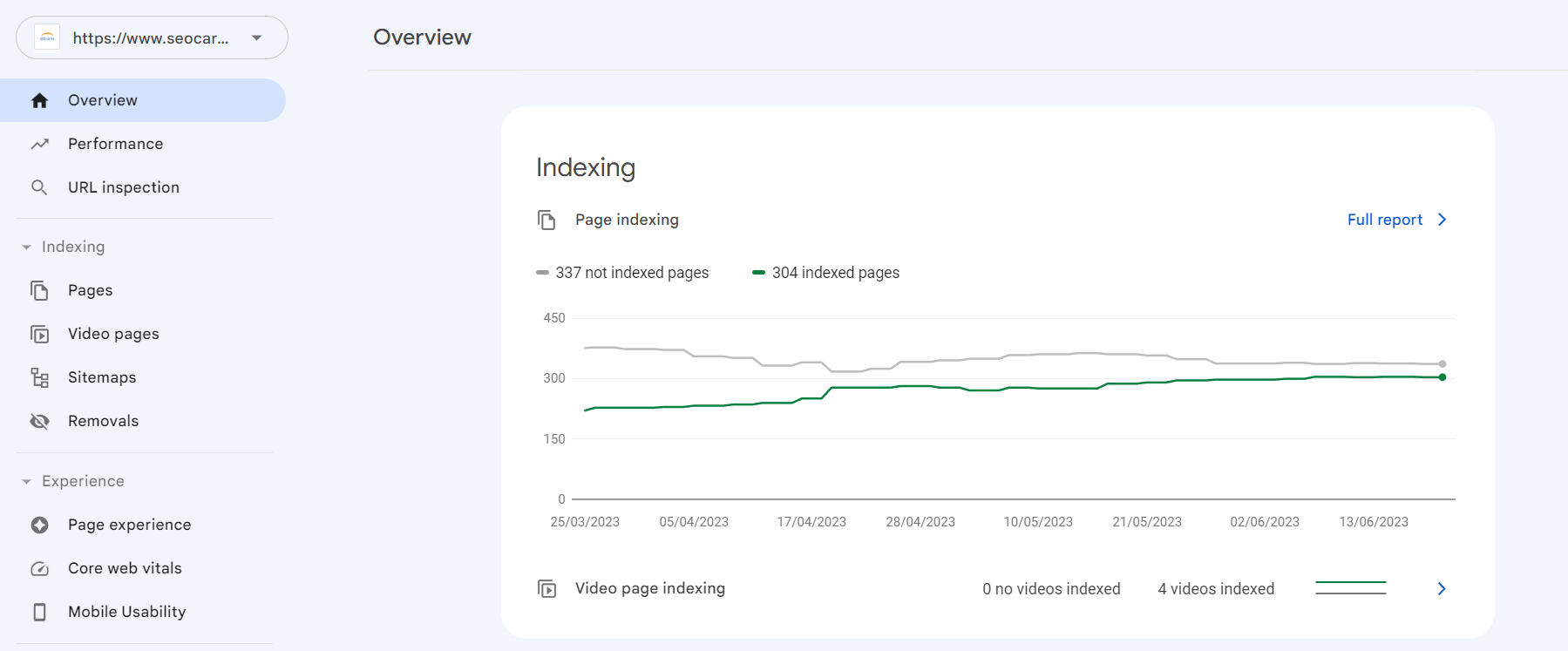
Watch for crawl errors:
Check for any errors that might prevent search engines from crawling certain pages. Fixing these issues improves the crawl budget.
Observe crawl behavior:
Keep an eye on how search engine bots interact with your website. Are they crawling important pages or spending time on less relevant ones?
What is the crawl budget formula?
The crawl budget formula is:
Crawl Budget = Crawl Rate + Crawl Demand
In this formula, the crawl budget is determined by adding the crawl rate (the number of pages a search engine can crawl per time unit) with the crawl demand (the popularity and importance of the pages on your website).
Does the size of a website impact its crawl budget?
Yes, the size of a website can impact its crawl budget.
Larger websites with more pages may take longer for search engines to crawl and index, potentially affecting how many pages get indexed.


